Understanding fixed index annuities
It’s time to rethink, and reframe, retirement
Understanding the basics
A fixed index annuity may help you reach your long-term financial goals. In exchange for your premium payment, the insurance company provides you an annuity contract designed to provide income. Interest crediting is based, in part, on the performance of a benchmark stock market index, to your account value. Fixed index annuities are designed to help provide income in retirement by helping accumulate assets that are not subject to market risk and turning those assets into a guaranteed income stream. You may choose to take the income available from your FIA immediately, or at some time in the future.
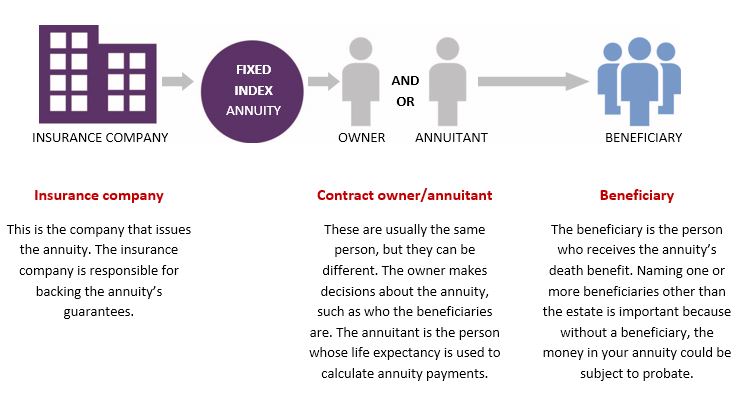
Interested parties in a fixed index annuity:
 Understanding the benefits
Understanding the benefits
A fixed index annuity (FIA) offers a unique combination of benefits that can help you achieve your long-term goals. No other product offers the tax deferral, indexed interest potential, protection of account value from market declines, and optional benefits to protect your retirement assets and income.
Let’s take a closer look as the three key benefits of fixed index annuities: tax deferral, indexed interest potential, and protection.
Tax deferral
Under current federal income tax law, any interest earned in your fixed index annuity contract is tax-deferred. You don’t have to pay ordinary income taxes on any taxable portion until you begin receiving money from your contract. Withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income and, if taken prior to age 59½, a 10% federal tax penalty may apply.
Indexed interest potential
Fixed index annuities provide an opportunity for potential interest growth based on changes in one or more indexes. Because of this potential indexed interest, FIAs provide a unique opportunity for accumulation. Since the interest your contract earns is tax-deferred, it may accumulate assets faster. Faster, because delaying, or deferring, when you pay income tax provides a mean to earn interest on your interest. In addition to potential indexed interest, FIAs can offer you an option to receive fixed interest.
Protection
Fixed index annuities offer you a level of protection you may find reassuring. That protection can benefit you in three separate ways:
- Accumulation: Your original principal and any additional premium, if credited interest, are protected.
- Guaranteed income: You and / or your spouse can be protected from the possibility of outliving your assets.
- Legacy: If you pass away before annuity payments begin, a fixed index annuity may help you provide for your loved ones, as your account value can be passed directly to your properly designated beneficiaries (avoiding probate). If you are in the distribution phase (taking your lifetime income), and you pass away, any remaining account value or, if purchased, the enhanced death benefit rider value can be passed directly to your properly named beneficiaries (probate avoidance depends on a properly named beneficiary other than the estate).
Guarantees are backed by the financial strength and claims paying ability of the issuing carrier.
Annuities are long-term products and may be subject to surrender charges and holding periods, which vary by carrier.
Tax deferral
A fixed index annuity offers tax advantages.
During the accumulation phase of your contract, any interest growth is tax-deferred. If you purchase your fixed index annuity with after-tax dollars, you will only pay ordinary income taxes on your earnings when you begin withdrawing money. Tax-deferred growth, compounded over time, may increase the amount of savings and income your fixed index annuity generates for you and/ or your spouse in retirement (if joint income is selected) because you are also getting that tax deferred growth and crediting on funds that may have otherwise been paid out in taxes.
Tax deferral is also a benefit of traditional IRAs and 401(k)s. However, annuities don’t have any government-imposed contribution limits. Because of that, they can often be a good supplemental choice if you want to save more than IRAs and 401(k)s allow, and still enjoy tax-deferred growth potential.
Purchasing an annuity within a retirement plan that already provides tax deferral results in no additional tax benefit. So use of an annuity to fund a qualified plan may be based upon features other than tax deferral. Features may include the ability to protect your accumulation value, which is comprised of your principal AND credited interest, or the desire for guaranteed lifetime income options, or the guaranteed death benefit.
How tax deferral can help
Tax deferral can be an effective part of your retirement strategy. For example, this chart shows how a $100,000 initial payment, compounded at 5% annually, grows tax-deferred. Twenty years later, after taxes are paid on the lump-sum distribution, the amount is still greater than the amount accumulated in a taxable product after 20 years.*
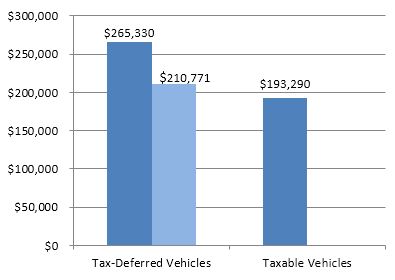 *Assumes a 33% ordinary income tax assessed yearly on taxable earnings and at the period end on tax-deferred earnings. Actual tax rates may vary from this example for different taxpayers and assets (e.g., capital gains and qualified dividend income). Actual performance of your contract will also vary. Hypothetical interest is not guaranteed and does not represent performance of any particular annuity. If a withdrawal or distribution is taken, the tax-deferred earnings would be reduced by income taxes on any interest and, if taken prior to age 59½, a 10% federal tax penalty may apply. Consider your personal retirement plan and income tax brackets, both current and anticipated, when making financial decisions.
*Assumes a 33% ordinary income tax assessed yearly on taxable earnings and at the period end on tax-deferred earnings. Actual tax rates may vary from this example for different taxpayers and assets (e.g., capital gains and qualified dividend income). Actual performance of your contract will also vary. Hypothetical interest is not guaranteed and does not represent performance of any particular annuity. If a withdrawal or distribution is taken, the tax-deferred earnings would be reduced by income taxes on any interest and, if taken prior to age 59½, a 10% federal tax penalty may apply. Consider your personal retirement plan and income tax brackets, both current and anticipated, when making financial decisions.
 Indexed interest potential
Indexed interest potential
Another advantage of a fixed index annuity is the opportunity to accumulate interest based on changes in an external index.
Some FIAs offer you a choice of indexes rather than just one. In addition to choosing your indexes, you can also determine what portion of your annuity’s value will be based on each index chosen.
Although an external market index or indexes may affect your contract values, the contract does not directly participate in any stock or equity investments. You are not buying shares of any stock or index fund.
FIAs’ indexed interest potential
When you purchase a fixed index annuity, you can allocate its value to one or more chosen indexes. A crediting method (which we will define later) is then used to track the performance of your index(es). At the end of each contract year, indexed interest is calculated.
If the result is positive, you will automatically receive indexed interest, subject to a participation rate, and a cap (which we will also define later). That interest is locked in each year, and cannot be lost due to index declines at some point in the future.
If the result is negative, nothing happens – and that can be good news! Although you won’t receive any indexed interest for the year, your annuity’s value doesn’t decline, you are simply credited “0%” that year.
Factors that influence how a FIA’s indexed interest is calculated
When you purchase your fixed index annuity, you can often choose the index(es) to which you allocate your annuity’s value. You can also often choose the crediting method used to track changes in your chosen index(es). Before we discuss those crediting method choices, let’s look at some other factors that will affect how your indexed interest is calculated.
Cap. Some fixed index annuities set a maximum rate of interest (or cap) that the contract can earn in a specified period (usually a month or year). If the chosen index increase exceeds the cap, the cap is used to calculate your interest.
For example, if the annual cap in a hypothetical example were 3.00% and the value of the index rose by 4.80%, the cap amount of 3.00% would be credited to your contract. However if the index change was only 2%, your contract would be credited 2%, since that is lower than our hypothetical cap.
Participation rate. In some annuities, a participation rate determines what percentage of the index increase will be used to calculate your indexed interest.
For example, let’s suppose the index rose by 10%. If a hypothetical FIA has a 75% participation rate, the contract would receive 7.5% in interest. (Participation rates are generally applied after caps, and before a spread). There are a number of fixed index products that have a 100% participation rate, however, these contracts will also use a cap to limit interest crediting. Before making a purchasing, be sure to review the contract to understand how interest is calculated as well as any guarantees.
Spread. The indexed interest for some annuities is determined by subtracting a percentage from any gain the index achieves in a specified period. For example, if the annuity has a 4% spread and the index increases 10%, the contract is credited 6% interest.
FIA crediting method choices:
No single crediting method consistently delivers the most interest under all market conditions.
Some of the more popular crediting methods are listed below. For a better understanding of how each crediting method works, talk to your financial professional. Keep in mind that caps, participation rates, and spreads will also enter into the calculation of indexed interest and may reduce the amount of interest credited.
Annual point-to-point. This method tracks changes in the market index from one contract anniversary to the next and credits interest based on that annual change.
Monthly sum (also referred to as monthly point-to-point). With this method, individual monthly increases and decreases in the index values are tracked and added up. Their 12 month sum helps determine the indexed interest credited to the annuity.
Monthly average. For this method, the individual monthly index values are totaled and then divided by 12 to find the average. The starting index value is subtracted from the average to determine the amount of positive or negative index change. This amount is divided by the starting value to determine the percentage of interest credited to the annuity.
The benefits of automatic annual reset
Annual reset is a common FIA feature. At the end of each contract year, your annuity’s index values are automatically reset. That means this year’s ending value becomes next year’s starting value. Annual reset also locks in any interest gains your contract earned during the prior year.
This chart shows how annual reset works.
A The index drops, but your contract value holds steady.
B Following a year of negative index performance, the market heads up. The index does not have to make up previous losses before your annuity can earn additional interest. Your accumulation value can increase in any year in which a positive index change takes place, thanks to annual reset.
This hypothetical example is provided for illustrative purposes only and does not reflect any surrender charges or rider fees that may be assessed. If there is no indexed interest, the value would be the money you put into the annuity.
Protection benefits
A third important advantage of a fixed index annuity is the range of guarantees and optional protection benefits available. These benefits allow you to transfer risk to the insurance company issuing the fixed index annuity. These guarantees help protect your assets, your retirement income, and your beneficiaries. In exchange for the risk transfer, the benefits may carry an additional cost that will vary by product and company.
Accumulation
Annuities are subject to surrender charge periods, which can vary, but are generally between five and 10 years in duration. As long as you abide by the terms of your contract, you will not lose any of the money you place in your annuity due to surrender charges. Additionally, any interest credited to the contract is locked in and protected as well.
Guaranteed income
A fixed index annuity puts you in control of your future income, based on the annuity you choose and how much money you put into it.
After your contract has had an opportunity to earn interest over its deferral period, you can begin distribution. You can then receive your contract’s values in a stream of income that will last your lifetime (or longer). The amount of your payments is based on the value of the contract on the date you begin distribution and the payout schedule you choose.
You generally have two choices for receiving income payments: annuitization payments or income withdrawals. For annuities that are funded with non-qualified money (after-tax money) not held in a qualified plan such as an IRA or a 401(k),) part of each annuitization payment is a tax-free return of what you paid for the annuity, and part is taxable as interest you earned on the annuity. On the other hand, income withdrawals under the same annuity are fully taxable until the interest you earned has been taxed. Then you withdraw what you paid for the annuity tax-free. It’s always a good idea to consult with your tax advisor before choosing between annuitization payments and income withdrawals.
Protection with income that can increase
As we noted, a FIA allows you to convert your annuity’s value into a series of fixed-amount payments. Depending on the product you choose, many FIAs go beyond this. They offer benefits or optional income riders with payments that can increase to help you keep pace with inflation throughout retirement.
Your income payments will be scheduled as withdrawals you can begin any time after you reach a certain age (often age 60). And with some FIAs, your income payments will be larger if you postpone taking them for a few years.
These income riders or benefits provide a valuable benefit, but they usually come at a cost. Your financial professional can discuss the income options, costs, and restrictions offered by the FIA you’re considering.
Please note that withdrawals may be subject to regular income tax and, if taken prior to age 59½, a 10% federal tax penalty may apply.
Legacy benefit
If you pass away before you begin to receive scheduled annuity payouts of the contract’s value, your beneficiary will receive a death benefit. In some cases, even if you pass away after you’ve begun to receive income from the annuity, it’s still possible your beneficiary will receive a death benefit. Your beneficiary may choose to receive your contract’s values in a single payment or in a series of payments over time.
The death benefit may be a reason some individuals purchase annuities even though they have no immediate plans to receive their contract values. They simply want to know the money is available should they need it (subject to contract provisions like surrender charges) – and that it can be passed on to their beneficiaries if they don’t use it.
Is a fixed index annuity right for you?
The answer is, “maybe.”
Only you know your goals for retirement, so only you can determine your needs. A fixed index annuity isn’t the right solution for everyone, and you shouldn’t buy one unless it’s appropriate for your situation.
You may want to consider a fixed index annuity if the following benefits are important to you:
- Tax deferral to help you reach your retirement goals
- Indexed interest potential to help accumulate your retirement savings
- Protection benefits that can help protect your retirement assets and income
Purchasing an annuity is an important decision, and one you should only make after consulting with your financial professional.
Guarantees are backed by the financial strength and claims paying ability of the issuing carrier.
For more information on fixed index annuities, talk to a licensed insurance professional.
Distributions are subject to ordinary income tax and, if taken prior to age 59½, a 10% federal penalty tax may apply.
● Not FDIC insured ● May lose value ● No bank or credit union guarantee ● Not a deposit ● Not insured by any federal government agency or NCUA/NCUSIF